Osteoarthritis and arthritis affect the joints and have similar symptoms. Therefore, they are often confused. Even their names agree, however, they are completely different diseases. If arthrosis destroys the joints, then arthritis causes an inflammatory process throughout the body. This is the fundamental difference between osteoarthritis and arthritis. Now in more detail.
The most important thing in arthritis
Arthritis is a progressive disease caused by infection, immune or metabolic disorders, hormonal disorders. There are over 200 varieties. The main symptom of arthritis is inflammation in the joint area, swelling, redness of the skin. In an advanced form, the disease causes complications on the heart, kidneys and liver. People aged 25 to 40 are at risk.

Symptoms of arthritis
The disease can be hidden. The first signs of arthritis are usually:
- Pain. It comes on suddenly and gets worse with movement. It is felt more intensely at night, after sleep, stiffness is felt;
- Tissue changes. Arthritis is characterized by swelling and redness of the skin, synovitis and bursitis are possible (in the first case it is an inflammation of the synovial membrane, in the second case of the joint sac);
- Temperature rise. As a rule, the temperature rises in the affected joints. A high body temperature (38-39 degrees) can also be observed.
Symptoms aggravate the manifestations of the inflammatory process:
- prostration;
- painful urination;
- chills;
- conjunctivitis.
If the symptoms are ignored, the disease will become chronic. As a result, the work of the internal organs will be disturbed, and the modification of the joints can lead to disability.
The most important thing in arthritis
Osteoarthritis is a non-inflammatory disease that leads to deformation and destruction of cartilage tissue. Cartilage covers the surface of the joint and prevents the bones from touching each other. When it is in order, the person moves freely and painlessly. The causes of the pathology can be different: heredity, deviations in the structure of the joints, injuries, excessive loads. Unlike arthritis, the disease affects only the joints.
Osteoarthritis usually develops in older people, as joint surfaces wear down with age. The disease also occurs in people whose occupation puts a lot of stress on the joints of the hands, wrists and legs. Therefore, arthrosis is also called "athlete's disease" or "pianist's disease".
Symptoms of arthritis
The disease is indolent. In the initial stage, symptoms may not appear. The first symptoms of osteoarthritis are usually the following:
- The joint is immobile after sleep or prolonged rest, but this quickly disappears with movement;
- Crackling, rattling, clicking - all this is accompanied by a dull sound;
- Pain with movement and exertion.
In the later stages of arthrosis, the symptoms are already noticeable: the joint becomes more immobile, pain appears, and the "hard joint" syndrome develops - soft cartilage tissue is replaced by bony growths. The development of the disease leads to immobilization of one or more joints.
Recognizable signs of arthritis and arthrosis
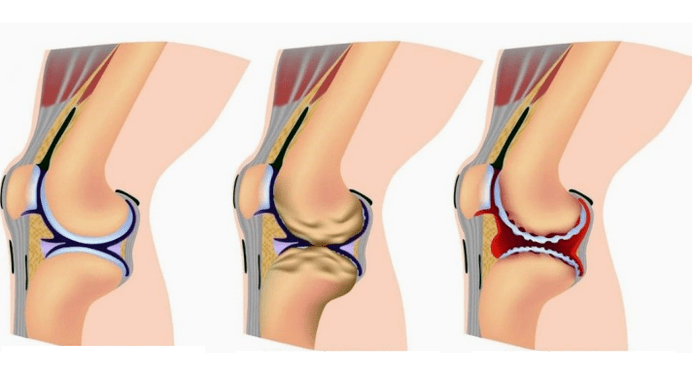
By carefully studying the symptoms and causes of arthrosis and arthritis, you can easily tell the difference. We combined the differences between the diseases to make this difference even more obvious.
trademark |
arthrosis |
Arthritis |
affected area |
Joints, cartilages, spaces between bones |
Joints, bones, internal organs: heart, liver, kidneys |
The nature of the disease |
Degenerate, destructive. Only the joints are affected |
Inflammatory. The disease affects internal organs |
Common causes |
Increased stress on the joints, heredity |
Severe infection, metabolic disorder |
Age |
It develops in people at a mature or advanced age. Risk factor - activities associated with excessive stress on the joints |
It develops in people aged 25-40, but it also occurs in adolescents and children |
Pain |
It is often a mild pain that occurs during movement and loading. In the later stages, the pain becomes more intense. |
The pain increases with movement, and is felt most strongly early in the morning. |
Crackling and screeching |
Dull clicks, dry screeching or screeching are characteristic |
It is not part of the features |
Deformation |
The joint is deformed, the inflammatory process is manifested |
There are seals, swelling, redness and increased temperature in the joint area. Deformation occurs if one disease has developed into another. |
Reduced mobility |
Arthrosis binds only the affected joint. |
Numbness in the whole body or in the joint |
Acute symptoms |
The joint "hardens" due to the formation of bony growths. In this case, the person can no longer move the leg or toes. |
High temperature - 38-39 degrees, conjunctivitis develops, breakdown and fever occur |
Development of symptoms |
It develops slowly, in the initial stage it is asymptomatic |
In the initial stage, there are symptoms of inflammation in the area of the affected joint. |
Prevention of arthritis and arthrosis
Disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Disease prevention includes:
- Moderate physical activity - fitness, swimming pool, skiing, cycling are suitable;
- Joint gymnastics - you can do it with a trainer in exercise therapy or stretch your joints at home;
- Proper nutrition - if there is a tendency to bone disease, it is worth giving up red meat and foods rich in fat. It is better to add more fruits and vegetables, fish and seafood to the diet. If you are overweight, you should follow a diet;
- Drink enough water - 2 liters a day. It is recommended to give up alcohol.
In order to reduce the risk of disease, doctors recommend wearing comfortable shoes, not sitting cross-legged, not catching a cold, and not succumbing to stress.
If you have symptoms reminiscent of arthritis or arthrosis, schedule an appointment at our Orthopedic Center. These diseases significantly reduce the quality of life, so it is important to diagnose them in time and start treatment.















































